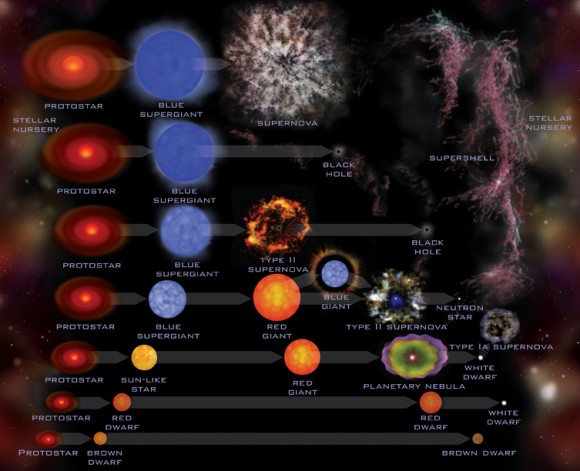
Stellar Life Cycle
Questions to Consider
*what is the life cycle of our star?
*what is the HR diagram?
*what are characteristics of each of the stellar stages?
*how do gravity and pressure affect one another through the life cycle of a star? How does the balance change through each stage?
* What is the main sequence?
* How does the brightness of our star change over its lifetime?
* How does the temperature of our star change over its lifetime?
How is the work of Annie Cannon connected to this system?
=====================
Tuesday:
Galaxy Intro
How accurate is Eric Idle's song? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Galaxy_Song
Seeing Galaxies takes some practice, so going to here will be a good start. It should take about 20 minutes to read through and see the galaxy types.
Next, go to the SDSS database, which took pictures for the first web site. You will be learning about galaxies, and going through the first 2 exercises and the first 4 questions. Take the time to collect the data on paper, and hand in what you have completed at the end of the hour.
==================Wednesday
SDSS
Read the opening paragraph of the Wikipedia article on the Sloan Digital Survey. (this should take 5 min)
Today, you will be doing a digital scavenger hunt with a partner. The activity is found here. (this should take 50-60 min, so take your time with the reading)
Note: the magnitudes are listed using 5 different filters-- u, g, r, i ,z Each of the filters is tracking different wavelengths. At this point, just write them down.
Get at least 10 of the questions answered.
=======================Thursday
4 Questions to Answer
Black holes:
http://www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/black-holes.html
http://www.environmentalgraffiti.com/sciencetech/understanding-black-holes-universe/6800
Please answer 4 of the following questions. Each answer should be at least 1/2 page long. Illustrations, as appropriate, may be included. Consider this a take-home test.
1. Will there ever reach a point in astronomy where we can stop spending money on telescopes and NASA? Consider the issues of space travel, human civilization, and distance and life cycles of stars. Provide at least 5 pieces of evidence, not just opinion, for your point of view.
2. Why is Annie Cannon a revolutionary person in the study of stellar spectra, and is luminosity more closely related to magnitude or absolute magnitude? What does the catalogue tell us about stars and the universe?
3. How is the HR diagram related to the formation and life cycle of stars? What does a HR diagram of a stellar cluster tell us about that area of space?
4. Compare three end points of a star (supernova, black hole, white dwarf, or neutron star) and tell me
how to recognize them, and why their original mass doomed them to their fate.
5. What role does the balance between gravity and pressure play in the formation and life cycles of stars, and how does this affect the formation of elements in the periodic table?
http://www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/black-holes.html
http://www.environmentalgraffiti.com/sciencetech/understanding-black-holes-universe/6800
Please answer 4 of the following questions. Each answer should be at least 1/2 page long. Illustrations, as appropriate, may be included. Consider this a take-home test.
1. Will there ever reach a point in astronomy where we can stop spending money on telescopes and NASA? Consider the issues of space travel, human civilization, and distance and life cycles of stars. Provide at least 5 pieces of evidence, not just opinion, for your point of view.
2. Why is Annie Cannon a revolutionary person in the study of stellar spectra, and is luminosity more closely related to magnitude or absolute magnitude? What does the catalogue tell us about stars and the universe?
3. How is the HR diagram related to the formation and life cycle of stars? What does a HR diagram of a stellar cluster tell us about that area of space?
4. Compare three end points of a star (supernova, black hole, white dwarf, or neutron star) and tell me
how to recognize them, and why their original mass doomed them to their fate.
5. What role does the balance between gravity and pressure play in the formation and life cycles of stars, and how does this affect the formation of elements in the periodic table?