Monday, April 29, 2013
Unit 5
http://www.livescience.com/space/
http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/features/news/grav_lens.html
Please read.
http://spiff.rit.edu/classes/phys230/lectures/planets/Lens_Nav.swf
Please do the exercises
Another look
What is Dark Matter?
Einstein Gravitational Lens
Day 2
Multiple Dimensions: String Theory (watch this video)
More about Einstein
Complete a 1-2 page reflection about Einstein and relativity by Friday based on the two links.
Friday, April 26, 2013
Telescopes
Find out an example ans a 2 sentence summary for each of the following types of telecopes. The link below is your priamry reources.
http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/resources/explorations/groundup/
Era stories:
Story 1
Galileo's Refractor: Galileo's telescope revealed the first hint of the depths of space. His dedication and approach to explaining what he saw revolutionized astronomy. (Includes one telescope story, one biography.)
Early Refractors: Telescopes with flatter lenses brought wider and clearer views of the sky but required longer tubes. Some refractors were so long that they became difficult to maneuver. (Includes two telescope stories.)
Great Refractors: New technology allowed astronomers to create larger lenses that produced bright, clear images. For a while, refracting telescopes became more popular than reflecting telescopes. (Includes three telescope stories, one biography.)
Story 2
Newton's Telescope: Sir Isaac Newton replaced the main lens of a telescope with a mirror, creating the reflecting telescope. (Includes one telescope story.)
Early Reflectors: Early reflecting telescopes used metal mirrors to look deep into space, but the new design presented new challenges. (Includes four telescope stories, one biography.)
Hugh Reflectors: Astronomers crafted telescope mirrors from glass instead of metal, making reflecting telescopes more powerful and easier to use. They began relying on photography and instruments to record observations. (Includes three telescope stories, two biographies.)
Story 3
Solar Telescopes: Solar telescopes are reflecting telescopes that use special instruments to observe the Sun. (Includes one telescope story, one biography.)
Radio Telescopes: The discovery of radio waves from space launched a new branch of study: radio astronomy. This spurred astronomers to develop new techniques to accommodate the large size of radio waves. (Includes two telescope stories.)
Multi-mirror Telescopes: Multi-mirror telescopes used computer technology to overcome the size limits of huge reflecting telescopes. (Includes two telescope stories, one biography.)
Space Telescopes: By placing telescopes in orbit above Earth, astronomers were finally free to view the universe in all wavelengths of light. (Includes five telescope stories, two biographies.)
http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/resources/explorations/groundup/
Era stories:
Story 1
Galileo's Refractor: Galileo's telescope revealed the first hint of the depths of space. His dedication and approach to explaining what he saw revolutionized astronomy. (Includes one telescope story, one biography.)
Early Refractors: Telescopes with flatter lenses brought wider and clearer views of the sky but required longer tubes. Some refractors were so long that they became difficult to maneuver. (Includes two telescope stories.)
Great Refractors: New technology allowed astronomers to create larger lenses that produced bright, clear images. For a while, refracting telescopes became more popular than reflecting telescopes. (Includes three telescope stories, one biography.)
Story 2
Newton's Telescope: Sir Isaac Newton replaced the main lens of a telescope with a mirror, creating the reflecting telescope. (Includes one telescope story.)
Early Reflectors: Early reflecting telescopes used metal mirrors to look deep into space, but the new design presented new challenges. (Includes four telescope stories, one biography.)
Hugh Reflectors: Astronomers crafted telescope mirrors from glass instead of metal, making reflecting telescopes more powerful and easier to use. They began relying on photography and instruments to record observations. (Includes three telescope stories, two biographies.)
Story 3
Solar Telescopes: Solar telescopes are reflecting telescopes that use special instruments to observe the Sun. (Includes one telescope story, one biography.)
Radio Telescopes: The discovery of radio waves from space launched a new branch of study: radio astronomy. This spurred astronomers to develop new techniques to accommodate the large size of radio waves. (Includes two telescope stories.)
Multi-mirror Telescopes: Multi-mirror telescopes used computer technology to overcome the size limits of huge reflecting telescopes. (Includes two telescope stories, one biography.)
Space Telescopes: By placing telescopes in orbit above Earth, astronomers were finally free to view the universe in all wavelengths of light. (Includes five telescope stories, two biographies.)
Wednesday, April 24, 2013
Monday, April 22, 2013
Stellar Evolution
Come up with a 1- 3 page creative story that creates an real-life analogy to our Sun's life cycle. This can be a detective mystery, or a an 8-12 page illustrated story book for a 4th grader. Your goal is to tell me about fusion, the stellar life cycle, the elements found in the stars, and the energy and neutrinos produced based on our work of the last week.
Stellar Life Cycle
Questions to Consider
*what is the life cycle of our star?
*what is the HR diagram?
*what are characteristics of each of the stellar stages?
*how do gravity and pressure affect one another through the life cycle of a star? How does the balance change through each stage?
* What is the main sequence?
* How does the brightness of our star change over its lifetime?
* How does the temperature of our star change over its lifetime?
How is the work of Annie Cannon connected to this system?
Stellar Life Cycle
Questions to Consider
*what is the life cycle of our star?
*what is the HR diagram?
*what are characteristics of each of the stellar stages?
*how do gravity and pressure affect one another through the life cycle of a star? How does the balance change through each stage?
* What is the main sequence?
* How does the brightness of our star change over its lifetime?
* How does the temperature of our star change over its lifetime?
How is the work of Annie Cannon connected to this system?
Monday, April 15, 2013
Starting Unit 3
Due to AA, I am postponing the test until tomorrow, Wednesday.
Take notes regarding:
The Sunspot Cycle (this should take 20 minutes to a half hour)
Maunder Diagram
Space Weather
Go to the link below. Try looking at a spectra that is 350 degrees, 1000 degrees, and 6000 degrees. What amount of visible radiation is shown in each of those? Why do we have blackbody spectra for stars?
Link: Black Body Radiation
==========Day 2
====
We watched excerpts from:
Learn360. 19 September 2012
http://www.learn360.com/ShowVideo.aspx?ID=128186
Learn360. 19 September 2012
http://www.learn360.com/ShowVideo.aspx?ID=227115
Complete the sun lab using the sheets provided, and the link shown below
Link: Sun Lab
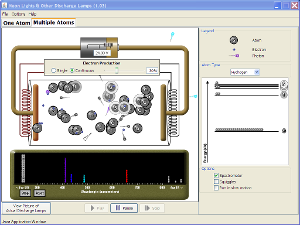
======Line Spectra=======
Line Spectra Lab
Investigate screen and experiment with the situations. Predict what will happen under the following situations:
What will happen when the voltage is increased?
With the voltage at a given amount, what will happen when the heater percentage is reduced?
If conditions are set so that light is being produced in multiple molecule mode, what will happen in single atom mode? Check your predictions.
Questions: 1. What condition(s) must be met in order for light to be produced by a discharge lamp?
2. What event(s) occurs to actually produce the light we see?
3. Does the spectrophotometer indicate unique spectrums for each gas?
4. What types of electromagnetic radiation are produced?
5. How could this phenomenon be used by astronomers?
=========
- Scan through the first 12 slides. Then, discuss the statement "Why is sunlight responsible for life on earth?" List what evidence you have that supports the statement.
- Focus on the radius and mass of the Sun and compare it to our Earth and Jupiter.
- Finally, look at the differences in temperature between the core and the convection zone, and try to explain it to me using a meaningful analogy. (Example: the difference between a tornado and a breeze is like a semi of rice grains compared to a dozen).
Take notes regarding:
The Sunspot Cycle (this should take 20 minutes to a half hour)
Maunder Diagram
Space Weather
Go to the link below. Try looking at a spectra that is 350 degrees, 1000 degrees, and 6000 degrees. What amount of visible radiation is shown in each of those? Why do we have blackbody spectra for stars?
Link: Black Body Radiation
==========Day 2
====
We watched excerpts from:
Citation (MLA)
The Sun. National Geographic. 2004Learn360. 19 September 2012
http://www.learn360.com/ShowVideo.aspx?ID=128186
Citation (MLA)
Secrets Of The Sun. A&E Television Networks. 2007Learn360. 19 September 2012
http://www.learn360.com/ShowVideo.aspx?ID=227115
Complete the sun lab using the sheets provided, and the link shown below
Link: Sun Lab
======Line Spectra=======
Line Spectra Lab
Investigate screen and experiment with the situations. Predict what will happen under the following situations:
What will happen when the voltage is increased?
With the voltage at a given amount, what will happen when the heater percentage is reduced?
If conditions are set so that light is being produced in multiple molecule mode, what will happen in single atom mode? Check your predictions.
Questions: 1. What condition(s) must be met in order for light to be produced by a discharge lamp?
2. What event(s) occurs to actually produce the light we see?
3. Does the spectrophotometer indicate unique spectrums for each gas?
4. What types of electromagnetic radiation are produced?
5. How could this phenomenon be used by astronomers?
=========
Thursday, April 11, 2013
Space Exploration R Us
Pick one of the gassy planets and make a power point.
Detail what we know about it on one slide.
Compare it to the Earth on a second slide.
Tell me about a mission to this planet. Include costs, findings, surprising information and what we have learned.
http://www.nasa.gov/missions/
http://www.nineplanets.com
Other countries--how have they figured in this?
http://www.planetary.org/explore/space-topics/outer-planets/
Should we have private space missions? ---could we head to outer planets
http://www.space.com/19077-big-space-missions-2013.html
Should they be manned or unmanned?--especially to the outer planets.
http://www.polaris.iastate.edu/EveningStar/Unit7/unit7_sub1.htm
The International Space Station--what we have done so far
http://www.russianspaceweb.com/iss_chronology_flights.html
Voyager
http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/
Cost of NASA
http://useconomy.about.com/od/usfederalbudget/p/nasa_budget_cost.htm
Detail what we know about it on one slide.
Compare it to the Earth on a second slide.
Tell me about a mission to this planet. Include costs, findings, surprising information and what we have learned.
http://www.nasa.gov/missions/
http://www.nineplanets.com
Other countries--how have they figured in this?
http://www.planetary.org/explore/space-topics/outer-planets/
Should we have private space missions? ---could we head to outer planets
http://www.space.com/19077-big-space-missions-2013.html
Should they be manned or unmanned?--especially to the outer planets.
http://www.polaris.iastate.edu/EveningStar/Unit7/unit7_sub1.htm
The International Space Station--what we have done so far
http://www.russianspaceweb.com/iss_chronology_flights.html
Voyager
http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/
Cost of NASA
http://useconomy.about.com/od/usfederalbudget/p/nasa_budget_cost.htm
Wednesday, April 10, 2013
Bits and Pieces of the Solar System
Two Orrery Views of the solar system
http://www.sunaeon.com
http://www.solarsystemscope.com
http://www.exploratorium.edu/ronh/solar_system/
===================================
How Far Have We Gone?
The Magnetosphere
Building a Moon
Asteroid Encounters
Space Junk
================Jovian Moons===============
Read pp. 162-162, 167-168, 185-186, p. 206, 210-12, 230
Galileo became a heliocentrist largely due to his observations about Jupiter's 4 biggest moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Using his telescope, he observed these moons and their patterns around the planet. He marked the motion of the moons in terms of Jupiter Diameters as viewed through his telescope.
Set up a Open Office Calc table with the names of the 4 moons at the top and the dates on the left side.
Gather data for at least 30 days using the Jupiter moon position applet a
Create a x-y scatter graph for each moon. PRINT OFF AND HAND IN.
Watch the movie.
http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/ess05_vid_galileomoon/
==========
Diameter of the Moon (at home lab for extra 10 points)
============Pluto as Planet Discussion at 2
Pluto isn't a planet
Pluto IS a planet
How was Pluto discovered?
http://www.sunaeon.com
http://www.solarsystemscope.com
http://www.exploratorium.edu/ronh/solar_system/
===================================
How Far Have We Gone?
The Magnetosphere
Building a Moon
Asteroid Encounters
Space Junk
================Jovian Moons===============
Read pp. 162-162, 167-168, 185-186, p. 206, 210-12, 230
Galileo became a heliocentrist largely due to his observations about Jupiter's 4 biggest moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Using his telescope, he observed these moons and their patterns around the planet. He marked the motion of the moons in terms of Jupiter Diameters as viewed through his telescope.
Set up a Open Office Calc table with the names of the 4 moons at the top and the dates on the left side.
Gather data for at least 30 days using the Jupiter moon position applet a
Create a x-y scatter graph for each moon. PRINT OFF AND HAND IN.
Watch the movie.
http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/ess05_vid_galileomoon/
==========
Diameter of the Moon (at home lab for extra 10 points)
============Pluto as Planet Discussion at 2
Pluto isn't a planet
Pluto IS a planet
How was Pluto discovered?
Thursday, April 4, 2013
Moon or Mars or Bust
Part 2: Planet rotation.
http://www.solarsystemscope.com/
http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/my-solar-system/my-solar-system_en.html
Monday:
You and your partner have a choice to make. Should the first off-Earth settlement be built on the Moon or on Mars? There are pros and cons to each.
To start, go to:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colonization_of_Mars
http://marshome.org/
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colonization_of_the_Moon
http://www.nss.org/settlement/
Now look at some of the missions:
http://planetary.org/explore/topics/the_moon/missions.html
http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/programmissions/
Use your Unit 2 readings to help you see if there are:
a) plate tectonics
b) a magnetosphere
c) an atmosphere
d) water
e) gravitational forces
f) minerals
g) temperature extremes
Come up with a list of up to 40 must-have items on your colonization effort. Also, be sure to tell me WHERE you plan on making your settlement (equator, a pole, etc.)
Wednesday, April 3, 2013
Phases of the Moon
Use the applet
Please sketch your answers to pages 1, 2, and 7 of the handout
===========================
Time Telling Questions.
Please sketch your answers to pages 1, 2, and 7 of the handout
===========================
Time Telling Questions.
- You look up in the eastern sky and see a waning gibbous moon rising. What time is it?
- As a savvy astronomy student, you know that some times of month have no moonlight at 1 am, which would be a perfect time for someone to break in and burglarize your prize green gumball collection. Name two phases of the moon which should concern you regarding this matter.
- Archeologists discover a strange religion that requires adherents to point their arms at the moon at 6 pm. Where should they be pointing at a full moon, a third quarter moon, a new moon, or a first quarter moon?
- Why does the side of the moon that is illuminated change from the right side to the left side over a period of 2 weeks?
- You notice the full moon is about 30 degrees west from the zenith of the sky. Give me an approximate time.
Tuesday, April 2, 2013
Wrapping up Unit 1
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dialogue_Concerning_the_Two_Chief_World_Systems
Video
********************
**************************
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)